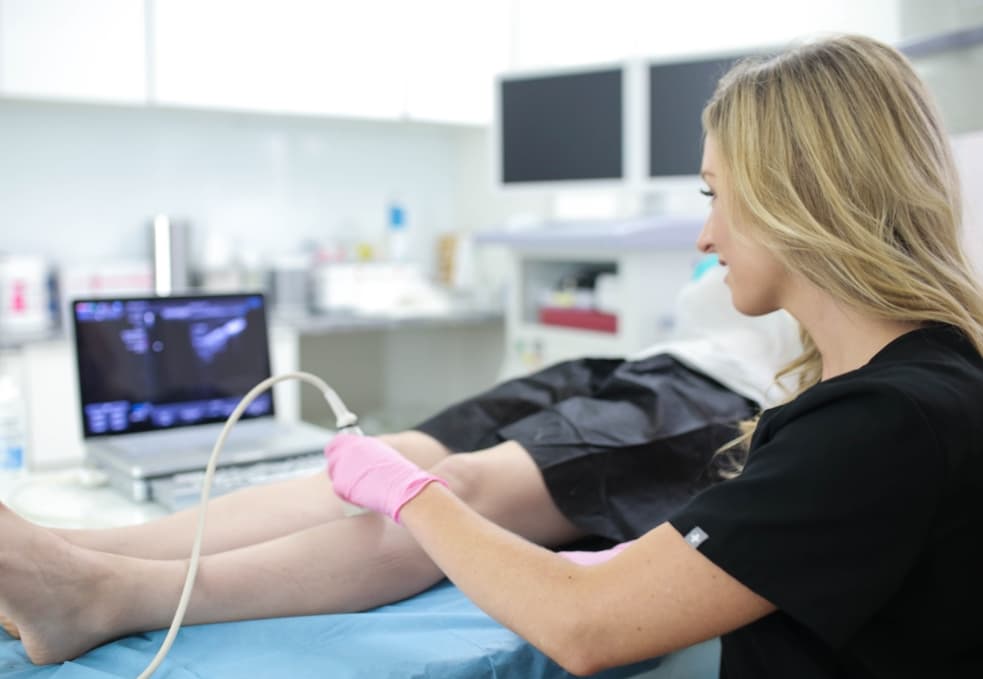
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT), you’re likely aware of the potential seriousness of this condition. DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms within a deep vein in the body, most commonly in the legs. If left untreated, DVT can be potentially life-threatening, so you must consult board-certified vein doctors immediately.
Long Island Vein Centers is led by some of the most talented, board-certified vein doctors in Long Island. Our vein doctors use the latest diagnostic techniques to identify the root cause of your vein problems, identify the blood clot, and curate a personalized minimally invasive treatment plan for deep vein thrombosis. Please schedule an appointment at your nearest vein center in Long Island for DVT treatments.
Symptoms of DVT:
- Pain and Swelling: One of the most common signs of DVT is pain and swelling in the affected leg. This can be accompanied by warmth and redness in the area.
- Blood Clot Symptoms: Some individuals may experience symptoms of a blood clot, such as tenderness or a feeling of fullness in the affected area.
- Leg Fatigue: Some people with DVT may feel unusually tired or fatigued in the affected leg.
- Cyanosis: In severe cases, DVT can cause cyanosis, a bluish or purplish discoloration of the skin due to reduced blood flow.
Diagnosing DVT
If you suspect you have DVT or experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. At Long Island Vein Center, we prioritize accurate diagnosis to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
- Clinical Assessment: Our vein doctors conduct a thorough clinical assessment, which includes discussing your medical history and performing a physical examination.
- Duplex Ultrasound: To confirm the presence of DVT, we utilize duplex ultrasound, a non-invasive imaging technique that allows us to visualize blood flow and identify clots within your veins. This step is crucial as it helps us accurately diagnose the condition.
Treatment Options for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Once diagnosed with DVT, you and your vein specialist at Long Island Vein Center will discuss the most suitable treatment options based on the severity and location of the clot, your overall health, and your personal preferences.
Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants)
- How They Work: Blood thinners, also known as anticoagulants, are medications that prevent the blood from clotting easily. They can help prevent existing clots from growing larger and new clots from forming.
- When Are They Used: Blood thinners are often prescribed as the initial treatment for DVT to prevent the clot from getting bigger and to lower the risk of a pulmonary embolism.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests are necessary while on blood thinners to ensure the medication is effective and that the blood is not too thin.
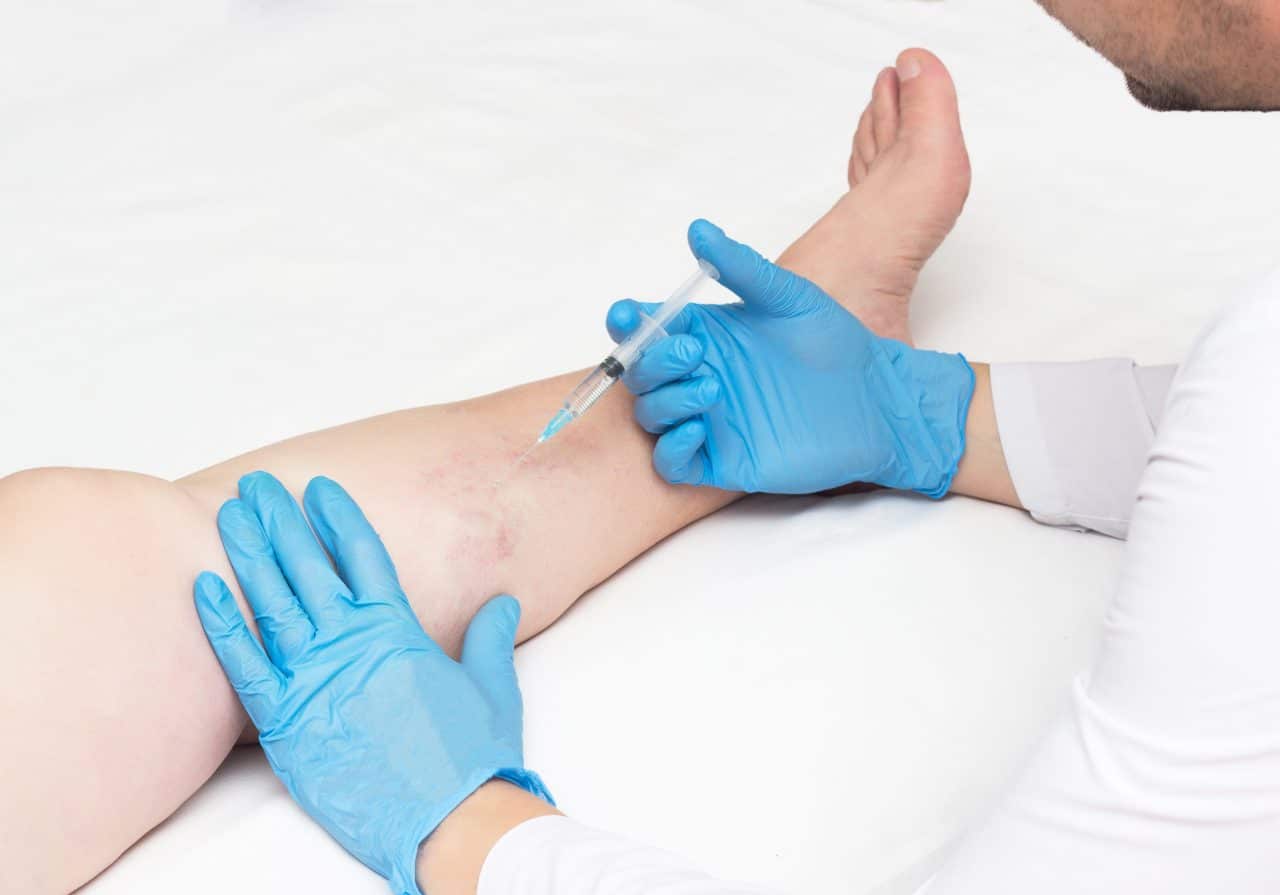
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA): EVLA is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to close off the affected veins responsible for deep vein thrombosis.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA involves the use of radiofrequency energy to heat and seal the affected veins responsible for the symptoms of DVT.
- VenaSeal Closure System: VenaSeal is a unique approach that uses a medical adhesive to seal the damaged vein shut, allowing blood to be rerouted through healthier veins.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Ambulatory phlebectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves the removal of varicose veins through tiny incisions. While it’s not typically used for DVT, it may be recommended for associated varicose veins.
Compression Stockings
- How They Work: Compression stockings are worn on the legs to help improve blood flow and reduce the risk of clot formation. They provide graduated pressure, with the highest pressure at the ankle, gradually decreasing as they move up the leg.
- When Are They Used: Compression stockings are often prescribed as a preventive measure or as part of the treatment plan for DVT. They can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Chronic Venous Insufficiency (CVI) Management
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a condition where the veins in the legs have difficulty returning blood to the heart. Venous insufficiency is often the root cause of deep vein thrombosis because the accumulation of blood in leg veins can lead to blood clots. It may require ongoing management to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Choosing the Best DVT Treatment
Selecting the most appropriate treatment for DVT depends on several factors, including the clot’s size, location, your overall health, and your preferences. At Long Island Vein Center, we prioritize a patient-centered approach to ensure you receive the best possible care.
- Severity: The choice of treatment may be influenced by the severity of your DVT. In more severe cases, a more aggressive approach may be necessary.
- Location of the Clot: The location of the clot within the deep vein network can also impact the choice of treatment. Some treatments may be more effective for clots in specific areas.
- Personal Health Factors: Your overall health, including any underlying medical conditions or medications you may be taking, can influence the treatment plan.
- Patient Preferences: We value your input and preferences when making treatment decisions. Your comfort and peace of mind are essential to us.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After the treatment, it’s crucial to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Regular follow-up appointments with our board-certified vein doctors at Long Island Vein Center are essential to ensure that your DVT is adequately managed. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, such as weight management, exercise, and dietary adjustments, to reduce the risk of future clot formation.
DVT FAQs
What causes deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
DVT is typically caused by the formation of blood clots in deep veins, often in the legs. Several factors can contribute to the development of DVT, including prolonged periods of immobility (such as long flights or bed rest), surgery, pregnancy, smoking, obesity, and certain medical conditions like cancer or genetic predispositions to clotting disorders.
How can I reduce my risk of developing DVT?
Reducing the risk of DVT involves lifestyle modifications and preventative measures. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Regular exercise and movement, especially during long periods of sitting.
- Maintain a healthy weight since being overweight or obese can increase your risk.
- Stay hydrated to maintain blood circulation.
- Avoid smoking as it can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Wear compression stockings to improve blood flow.
What are the symptoms of DVT?
The symptoms of DVT can vary but often include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected leg, typically the calf or thigh.
- Warmth and redness in the affected area.
- Tenderness or a feeling of fullness in the leg.
- Leg fatigue or heaviness.
It’s important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience these symptoms, as untreated DVT can lead to serious complications.
How is DVT diagnosed?
Diagnosing DVT typically involves a combination of clinical assessment and imaging tests. Your doctor will discuss your medical history and perform a physical examination. The gold standard for diagnosis is duplex ultrasound, a non-invasive imaging test that can visualize the blood flow and identify clots within the veins.
Are there any complications associated with DVT?
Yes, untreated or inadequately treated DVT can lead to serious complications. The most concerning complication is a pulmonary embolism, where a clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, potentially causing a life-threatening situation. Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and post-thrombotic syndrome are other complications that can result from DVT.
What are the advantages of minimally invasive treatments for DVT?
Minimally invasive treatments, such as endovenous laser ablation, radiofrequency ablation, VenaSeal, and ClariVein, offer several advantages, including:
- Reduced risk of complications compared to traditional surgery.
- Quicker recovery times.
- Less pain and discomfort.
- Smaller incisions or no incisions at all.
- High success rates.
Can DVT be prevented after surgery or during long flights?
For individuals at higher risk of DVT due to surgery or long periods of immobility, preventative measures are essential. Your doctor may recommend blood-thinning medications or mechanical compression devices to enhance blood flow during these situations. Staying well-hydrated, moving your legs, and avoiding prolonged sitting can also help reduce the risk.
Is DVT treatment covered by insurance?
The coverage for DVT treatment may vary depending on your insurance plan and the specific treatments recommended by your healthcare provider. At Long Island Vein Center, we offer free insurance verification even before your first appointment to help you understand your coverage and any potential out-of-pocket costs. We work closely with insurance providers to ensure you receive the best possible care.
Visit Long Island Vein Center for DVT Diagnosis & Treatment
At Long Island Vein Center, our board-certified vein doctors are committed to providing you with the best care possible. We offer a range of minimally invasive treatment options tailored to your specific needs. If you suspect you have DVT or have been diagnosed with it, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Contact Long Island Vein Center today to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards the best treatment for deep vein thrombosis.